Introduction to Cross-Platform App Development
Today’s chosen theme: Introduction to Cross-Platform App Development. Build once, deliver everywhere—without losing the quality, performance, or polish users expect. Explore frameworks, architecture, design patterns, testing, and release strategies that help you ship confidently. Have questions or experiences to share? Join the conversation and subscribe for hands-on guides.
What Cross-Platform Really Means
Cross-platform development means sharing as much business logic, UI, and tooling as practical, while honoring differences in platform behavior. You will still navigate platform quirks, but well-chosen frameworks and architecture can unlock significant reuse, faster iteration, and consistent brand experiences across devices.
What Cross-Platform Really Means
A small café chain built an ordering app with Flutter, launching on iOS and Android in eight weeks. They reused payment flows, loyalty logic, and design tokens, while swapping minor platform-specific integrations. Their first-week update fixed issues everywhere at once, surprising the team with momentum.
Choosing Your First Framework
Flutter in Practice
Flutter compiles ahead-of-time for mobile, offering fast UIs, a rich widget system, and predictable rendering. Teams love hot reload and design consistency. If you value pixel-perfect control and a strong component ecosystem, Flutter is a compelling first choice worth prototyping within your context.
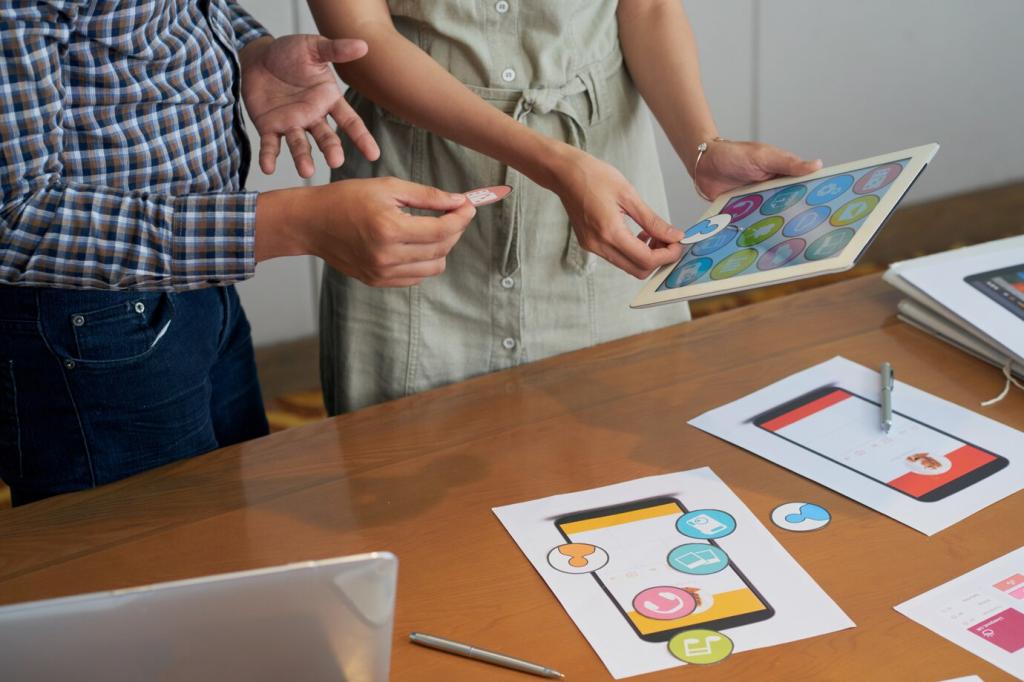


React Native In The Wild
React Native leverages JavaScript and React patterns, easing onboarding for web-focused teams. Performance improves with the new architecture and TurboModules, while community packages speed delivery. If you already live in React, this path reduces friction and aligns well with shared web expertise.
Project Setup and Architecture
Separate core business logic into a shared module, and isolate native bridges in thin adapters. Keep platform-specific code constrained to integration points like camera, biometrics, or deep platform APIs. This structure keeps the majority of your codebase portable and easier to test thoroughly.
Project Setup and Architecture
Choose predictable state management early. MVVM, Redux-like patterns, or BLoC can provide clarity across screens and platforms. A consistent state approach reduces bugs, simplifies testing, and lets new contributors ramp faster by understanding data flow and side effects at a glance.
Project Setup and Architecture
Design with flaky connectivity in mind. Cache essential data, queue writes for later sync, and handle conflicts gracefully. By embracing offline-first patterns, you deliver reliability users feel immediately, regardless of platform, network conditions, or the size of your growing feature set.

Designing for Platforms Without Losing Soul
Navigation bars, gestures, and system components carry user expectations. Embrace platform look-and-feel where it matters—back behavior, tab bars, menus—while retaining a shared design language through color, typography, spacing, and iconography. This balance feels native without fragmenting your codebase.
Render Pipelines Explained
Flutter paints via its own rendering engine, while React Native uses a bridge to native views. Understand your framework’s pipeline to identify bottlenecks. Optimize widget rebuilds, avoid unnecessary renders, and profile transitions that feel janky, especially on mid-range or older devices.
Reducing Bridge Chatter
In bridge-based stacks, minimize chatty calls across boundaries. Batch updates, memoize computed values, and push heavy work off the main thread. Aim for fewer, bigger operations so your UI remains fluid, taps feel instant, and scrolling maintains a steady, confident frame rate.
Measuring What Matters
Instrument startup time, first interactive paint, scroll smoothness, and navigation latency. Use built-in profilers, logs, and performance overlays to diagnose hot spots. Share dashboards with the team and celebrate wins—visible metrics keep momentum high and priorities grounded in user impact.

Unit, Widget, and Integration Tests
Protect your core logic with unit tests. Validate UI behavior with component or widget tests. Exercise full flows with integration tests on real devices. This layered approach catches regressions early, saves late-night firefighting, and keeps cross-platform features aligned across environments.

Continuous Delivery Pipelines
Automate builds for iOS and Android, sign artifacts securely, and run tests on device farms. Use pipelines to gate releases, generate changelogs, and notify stakeholders. A disciplined CI/CD flow makes shipping routine, freeing your team to focus on quality and customer insight.

Feature Flags and Staged Rollouts
Ship safely by toggling features for small cohorts, monitoring metrics, and ramping gradually. Staged rollouts reduce risk, enable rapid rollback, and let you learn from real usage. Invite readers to share their rollout playbooks or subscribe for our upcoming step-by-step setup guide.
Publishing and Maintenance
01
Store Requirements and Review Timelines
Prepare privacy disclosures, screenshots, and accurate metadata for each platform. Apple reviews can add time; Google’s tracks support faster iteration. Plan buffers for approvals, and communicate timelines with stakeholders so your roadmap remains credible and deliverable under real constraints.
02
Update Strategies That Respect Users
Bundle focused updates, write human-centered release notes, and avoid breaking changes. Consider phased releases paired with analytics to validate improvements. Encourage users to enable auto-updates and subscribe here for reminders when we publish new best practices and postmortems from real launches.
03
Observability and Crash Triage
Integrate crash reporting, structured logs, and performance traces from day one. Triage with severity, detect duplicates, and confirm fixes before closing. Share lessons learned with the team—and with our community by commenting your approaches to alerting, dashboards, and on-call playbooks.
Your Learning Path and Community
Week one: scaffold an app and choose your framework. Week two: implement navigation, state, and basic theming. Week three: add networking, caching, and tests. Week four: optimize performance and ship a beta. Subscribe for a printable checklist and sample repository links.
Your Learning Path and Community
Join forums, meetups, and open-source communities around Flutter, React Native, or .NET. Ask questions, share snippets, and contribute docs. Real-world guidance shortens your learning curve, and your voice helps others avoid common pitfalls while building confidence in cross-platform choices.